Mechanical ventilation is increasingly important in maintaining a safe and comfortable broadcast environment. One solution to achieve this is using heat recovery units, which can be found in more detail on our blog.
The heat recovery unit is responsible for recovering heat from the used air, achieved through a mechanical actuation system. Properly selecting the fans for the HRU is crucial to ensure the system operates intelligently.
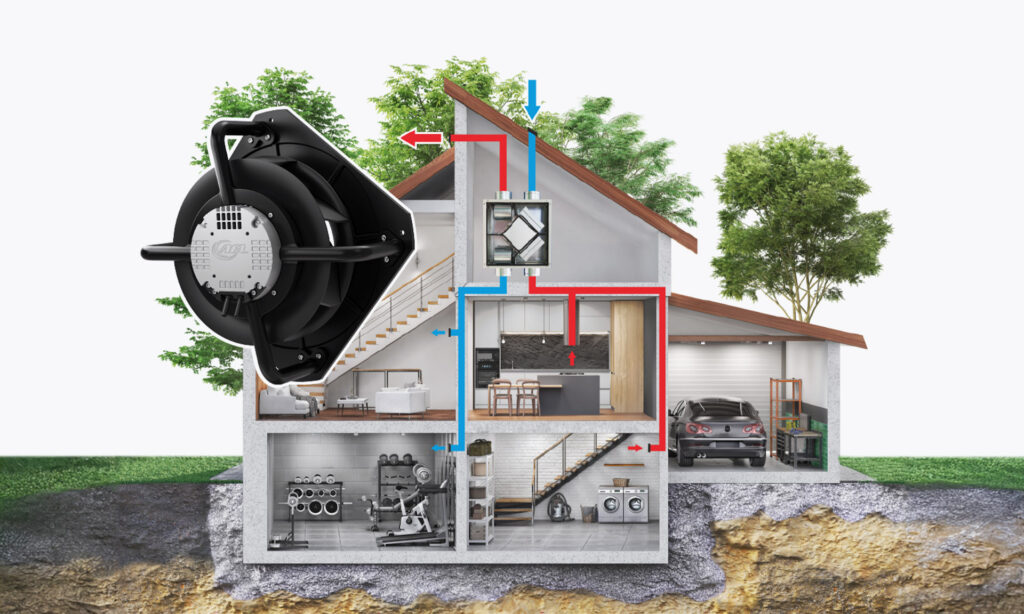
When selecting a heat recovery unit fan, the primary consideration is the operating point required. This refers to the designed air stream required to overcome the resistance of the flowing medium.
The device’s efficiency is determined by the demand for fresh air in the building. The flow resistance created by the HRU elements must be overcome to deliver the required amount of air. These elements include a heat recovery exchanger, air filters, and an air heater or cooler. All of these components contribute to the flow resistance that the fan must overcome to pump air.

Additionally, a network of ducts, air vents, and an air intake and exhaust vent create resistance.

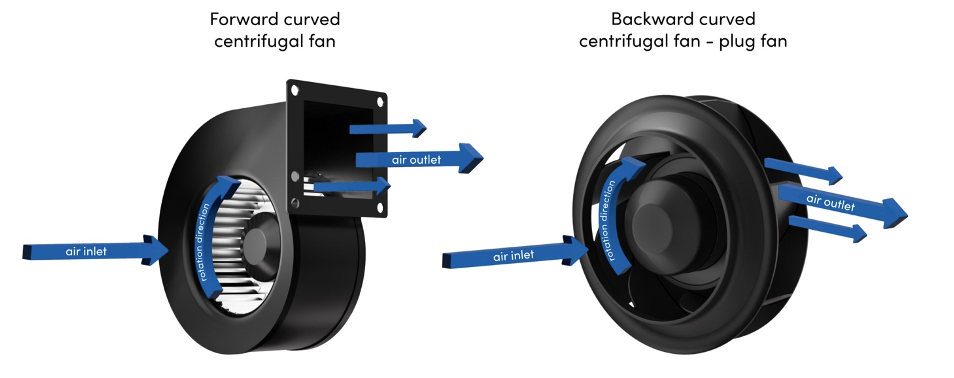
Design is an important consideration when selecting the right fan. Centrifugal fans with forward or backward bent blades are often used since they can handle the relatively high resistance created by the ventilation system.
The shape and size of the fan are important in terms of design. The desire to limit the dimensions of the heat recovery unit also requires the use of the most compact fans possible.
When selecting a fan, the type of engine it uses is an important factor to consider. AFL provides fans with DC, AC, and EC motors. However, the most commonly used fans are those with energy-saving EC motors. These motors are brushless and electronically commutated, with built-in electronics that enable easy, efficient, and smooth 0-10V/PWM signal control. Using EC motors, we can easily meet the increasingly stringent requirements for energy efficiency.
EC engines are highly efficient, even at reduced rotational speed, making them ideal for heat recovery units. This translates into significant energy cost savings, especially when compared to devices that have variable operating parameters, where the fans may operate at reduced efficiency for extended periods of time. Additionally, fans with EC motors are designed to take up less space and are quieter and lighter than fans with AC motors. Moreover, they come with capacity control devices that increase efficiency.
BACKWARD CURVED CENTRIFUGAL FANS
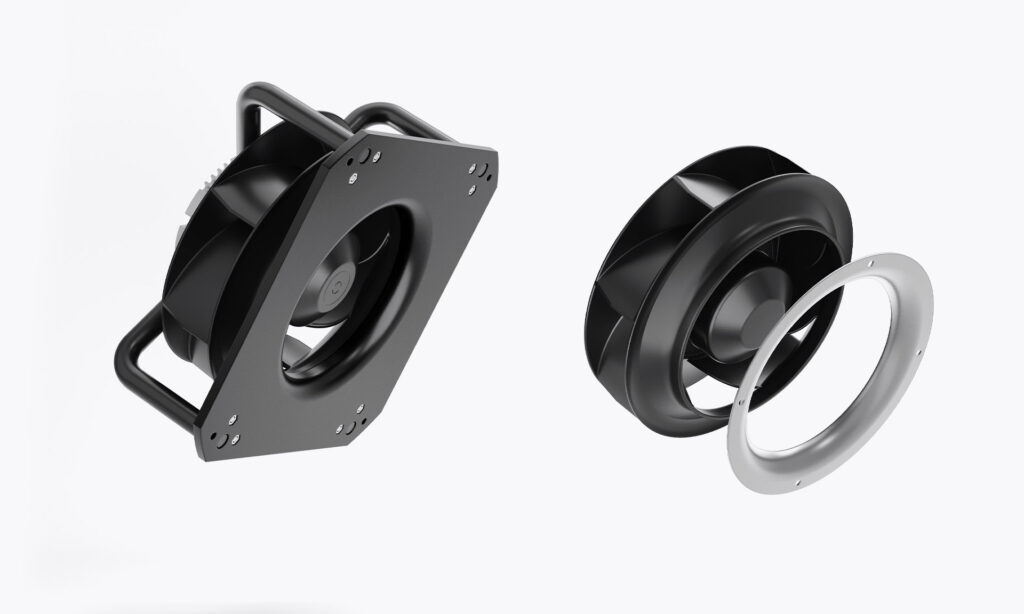
The most commonly used fans in HRUs are backward-curved centrifugal fans with backward-bent blades and EC engines. These are reliable and versatile designs suitable for modern heat recovery units.

To facilitate and speed up installation, backward fans with an integrated funnel and mounting plate are often used (marked as Backward Curved Centrifugal Fan+ in the AFL offer).

Manufacturers are now equipping heat recovery units with automatic flow balancing systems to maintain constant efficiency despite varying flow resistance, such as varying degrees of filter contamination. Measuring stubs are utilized at the fan inlet funnel in the case of backward curved centrifugal fans, along with additional sensors for measuring pressure, all working together with the regulation system.
FORWARD CURVED CENTRIFUGAL FANS
When it comes to HRUs, consider using forward-curved centrifugal fans. Some F3P series forward-curved centrifugal fans come equipped with built-in Constant Flow modules. This module allows the fan to maintain a constant airflow stream through real-time measurement of fan operating parameters and an advanced control algorithm. This means there’s no need for additional pressure measurement or fan performance control systems, making the system more straightforward and more cost-effective.
Author: Grzegorz Perestaj, Regional Sales Director, AFL MOTORS
