Centrifugal fans are among the most crucial components used in ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems. They are characterized by airflow that moves perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the impeller, enabling them to generate higher pressure than axial fans. These fans are recommended for projects requiring high efficiency and high resistance in the system. Although their design may vary in detail depending on the application and manufacturer, it is based on several fundamental elements. Below is an overview of the main components of a centrifugal fan and their roles in the device’s operation.
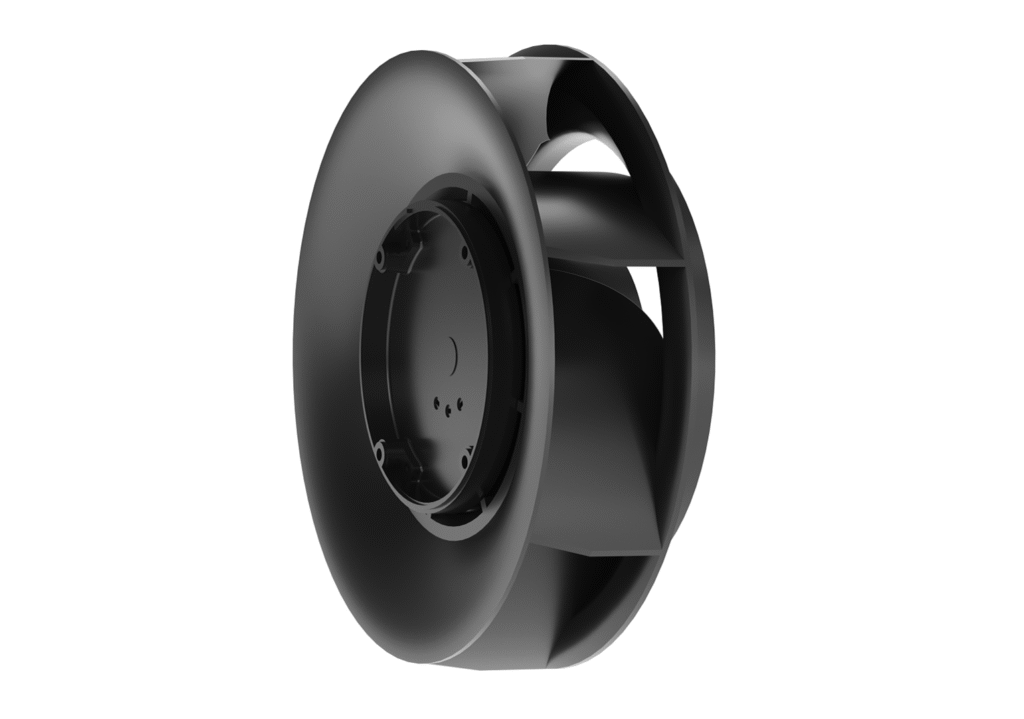
1. Impeller
The impeller is the most crucial part of the fan, responsible for moving the air. There are three main types of impellers used in radial fans:
- Backward curved – with blades curved backwards, ensuring high efficiency and low susceptibility to motor overload. Most often used in modern HVAC systems, where high efficiency is needed at high installation resistance.
- Forward curved – with blades tilted forward, used where high compression and quiet operation of fans are needed.
- Radial (straight) – with blades arranged radially, used mainly in dusty or industrial environments where resistance to contamination is crucial.

2. Motor
The core component of a centrifugal fan is the motor, which drives the impeller into motion. There are two primary types of motors:
- Asynchronous (AC) motor – a common solution, often used in simple applications, with a constant operating speed.
- EC (Electronically Commutated) motors – modern, brushless, energy-efficient units with integrated control electronics that enable smooth speed adjustment and seamless integration with building automation systems (BMS).

The motor can be integrated with the rotor (compact design) or separated by a drive shaft bearing.
3. Housing and mounting console
The housing of a radial fan serves multiple functions: it guides the airflow, reduces pressure loss, and dampens noise. Its shape and design influence the efficiency and stability of the device.
The most common types are:
- Spiral housings (scroll housing) – direct air to the outlet at a 90° angle to the inlet, facilitating the generation of static pressure in forward-curved fans.
- Plug fan consoles (without a spiral housing) – typically used in ventilation units and heat recovery units, where the fan is mounted directly on the device structure.
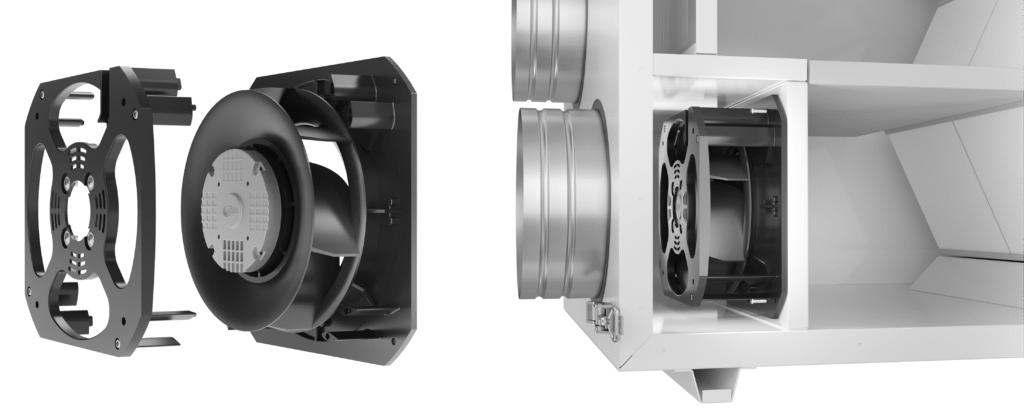
The housing material is usually galvanized steel, stainless steel, or plastic (e.g., in versions with increased chemical resistance).
4. Air inlet and outlet
Centrifugal fans feature a single central axial inlet, where air enters along the axis of rotation, and a radial outlet, where air exits at a right angle to the axis. The impeller’s axis of rotation is perpendicular to the direction of the compressed air flow.
At the fan inlet, suitably profiled suction funnels are used to optimize air flow and can optionally be equipped with elements such as protective nets, flow, or temperature sensors.
5. Damping and safety features (optional)
Depending on the application, centrifugal fans can also be equipped with additional elements, such as:
- Vibration dampers (shock absorbers, pads)
- Protective grilles
- Additional components for operation control and steering, such as temperature sensors, vibration sensors, and pressure sensors
6. Control System
In the case of EC motors, the control automation is integrated into the device.
It allows for:
- Smooth regulation of rotational speed (signal 0-10 V, PWM).
- Communication with BMS, typically via Modbus RTU, includes monitoring parameters such as power consumption, temperature, and operating time, along with error and alarm signaling.

In traditional AC solutions, control is achieved using external inverters (VFD) or transformers.
Summary
The centrifugal fan is a vital component of the ventilation system. Selecting the correct impeller type, motor, and technical specifications for a specific application is essential. Modern models with EC motors are now prevalent in the HVAC industry, offering improved efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and advanced control options.
Thanks to their modular design and versatile configurations, centrifugal fans are employed across nearly all industries and construction sectors.

Author: Marek Skarżyński, Technical Support Manager, AFL MOTORS
